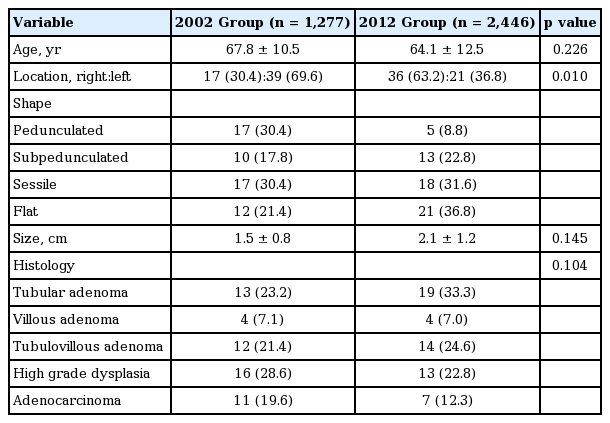
Colon Polyp Size Chart

Depending on their size and location in the colon.
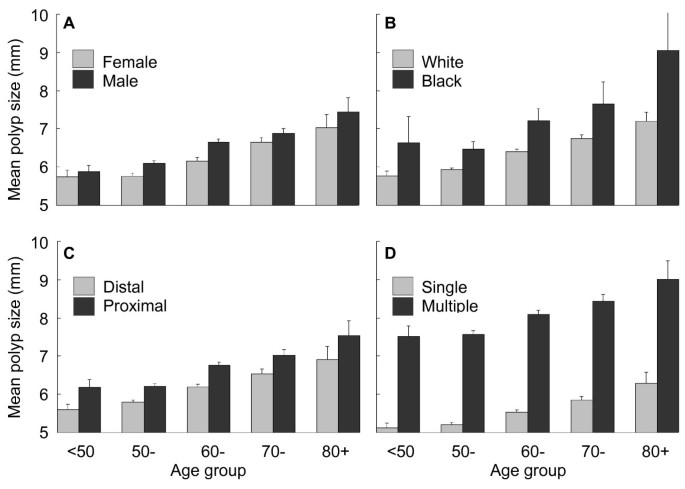
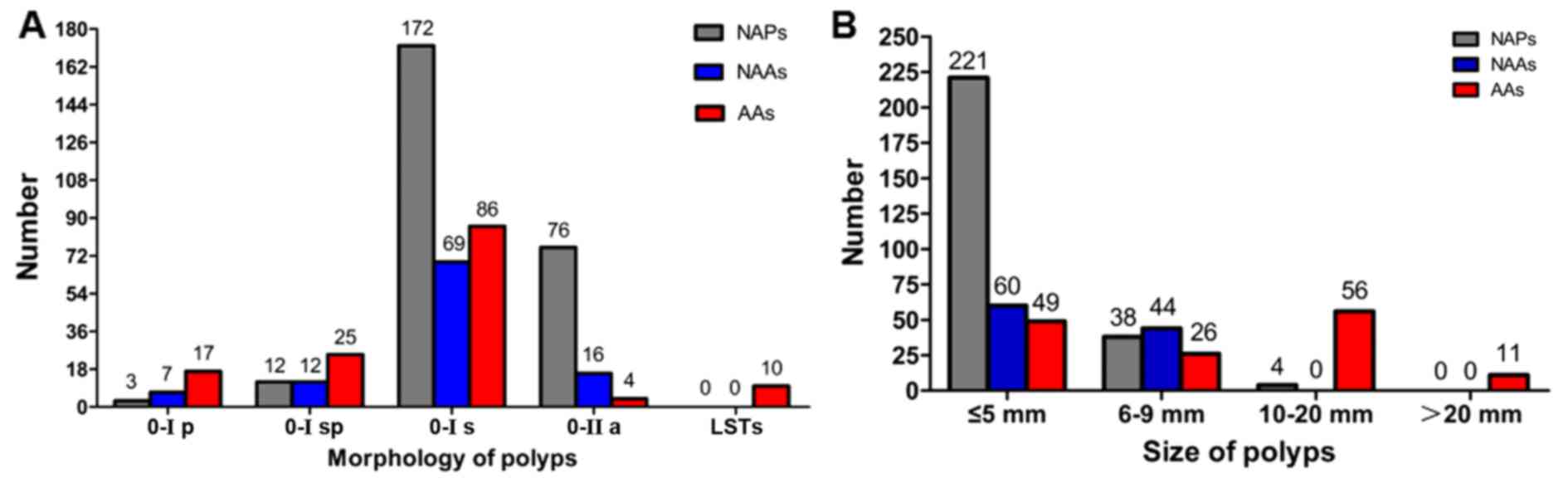
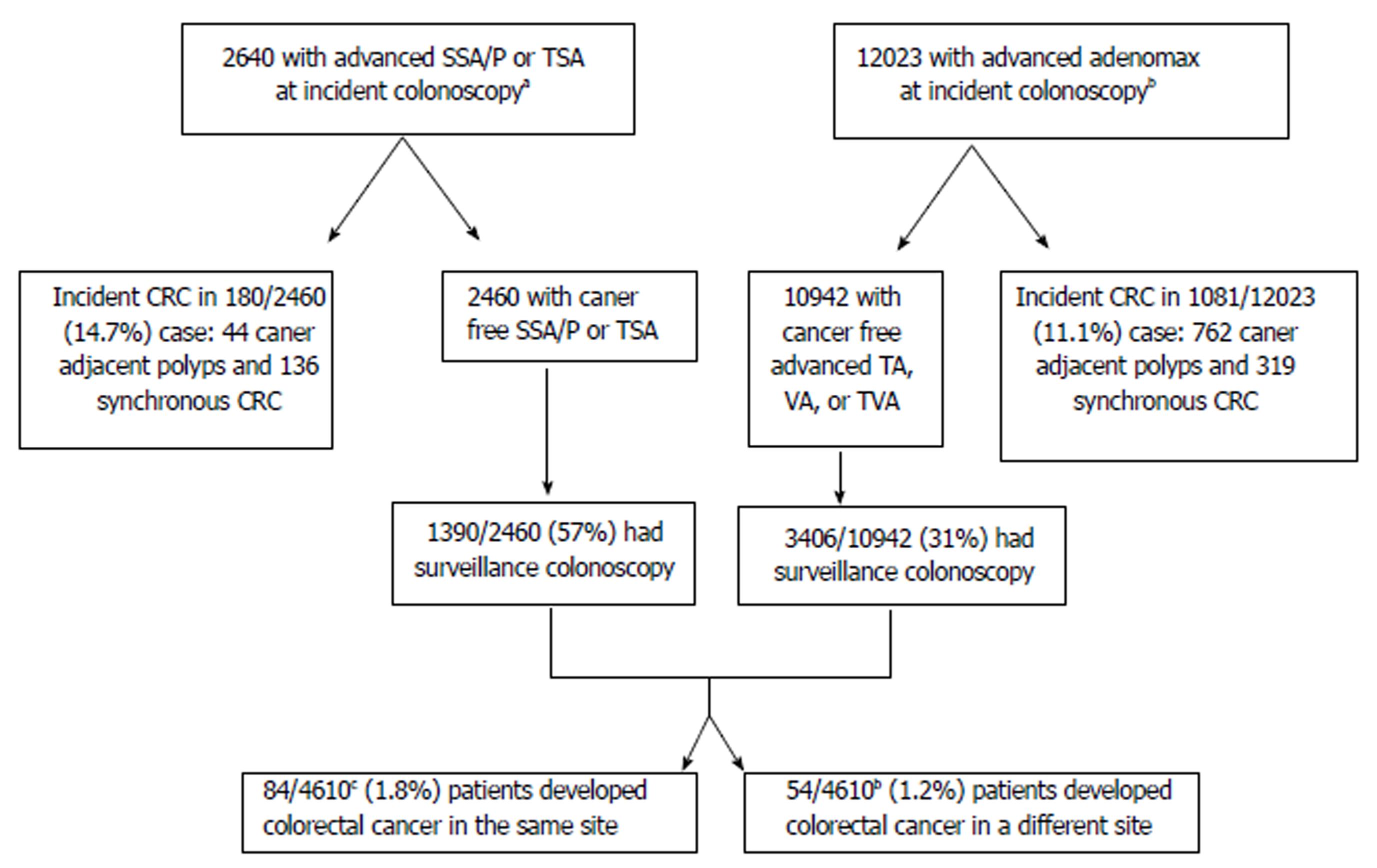
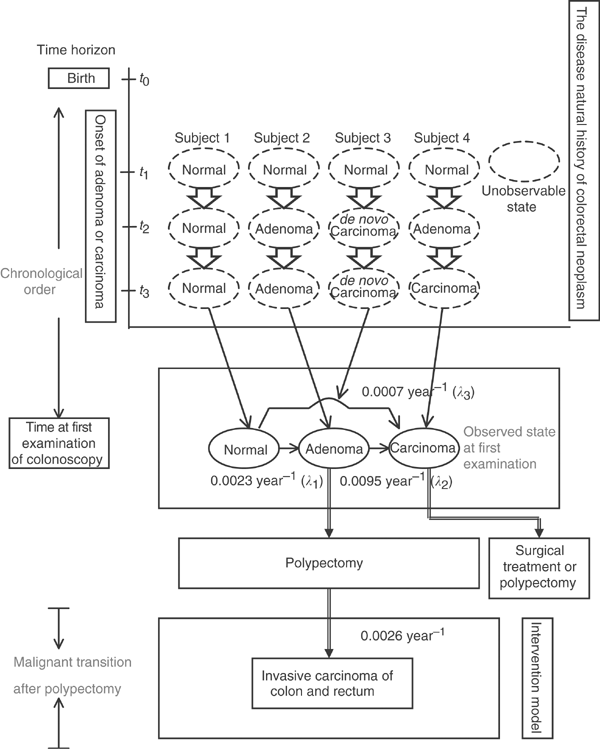
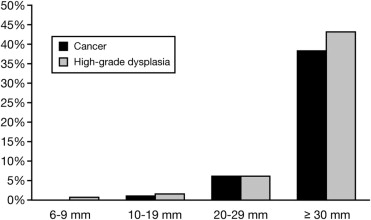
Colon polyp size chart. Polyps less than 1 centimeter in size have a slightly greater than a 1 chance of becoming cancer but those 2 centimeters or greater have a 40 chance of transforming into cancer. If it is attached without a stalk it is said to be sessile polyps are commonly found in the colon stomach nose ear sinus es urinary bladder and uterus they may also occur elsewhere in the body where there are. In general the larger a polyp the greater the risk of cancer.
Polyps don t always become cancerous but your risk of developing cancer increases with the number and size of colon polyps you have. Polyps are common in american adults and while many colon polyps are harmless over time some polyps could develop into colon cancer. But they also have the nasty habit that they degenerate in the base where they are attached to the colonic mucosa.
If you have had an adenomatous polyp or a serrated polyp you are at increased risk of colon cancer. A personal or family history of polyps puts you at higher risk for colon cancer as well. Polyps are benign non cancerous growths but cancer can start in some types of polyps.
But over time some colon polyps can develop into colon cancer which is often fatal when found in its later stages. Polyps growth slowly in diameter and in length. The size of a polyp typically does make a difference.
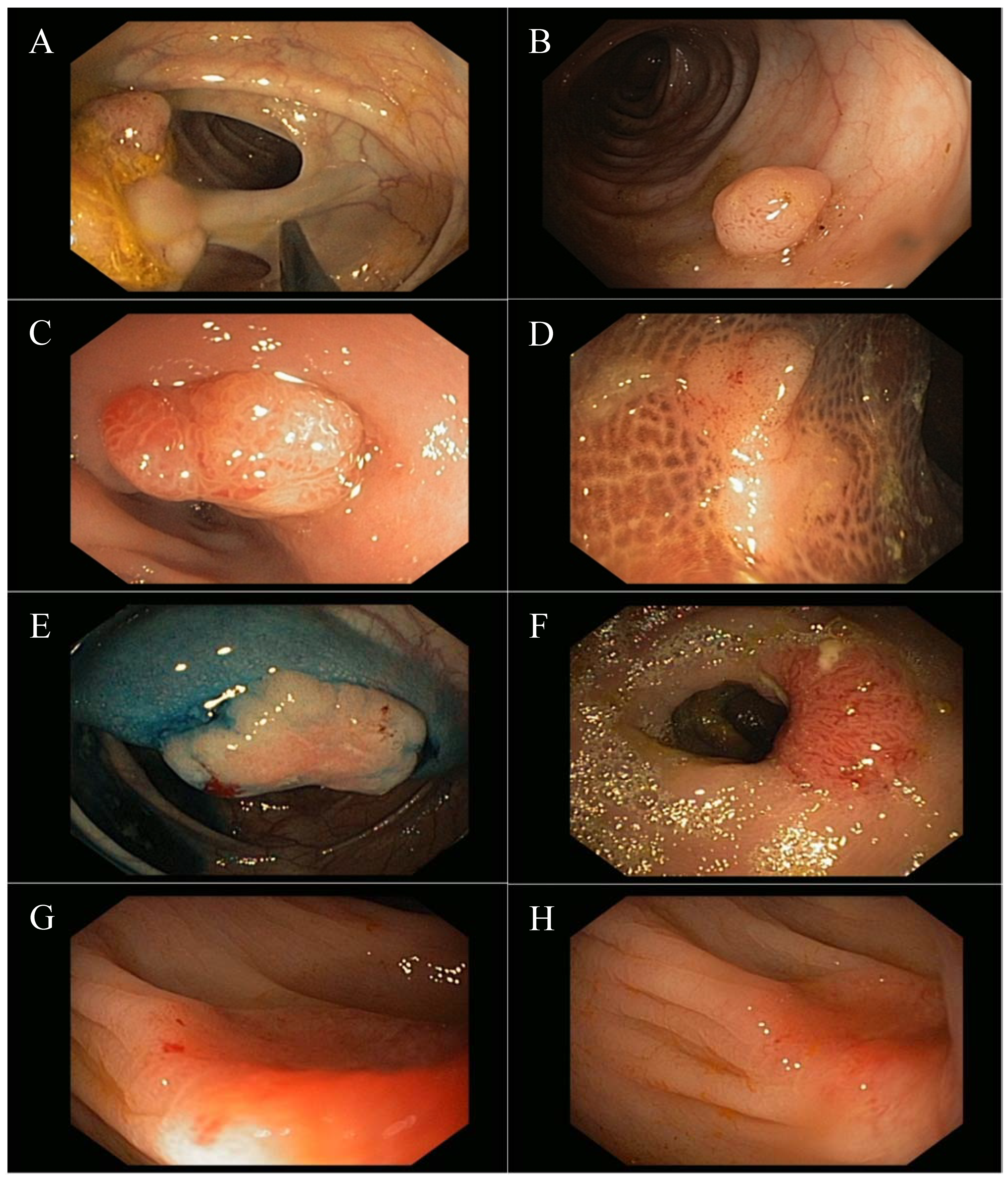
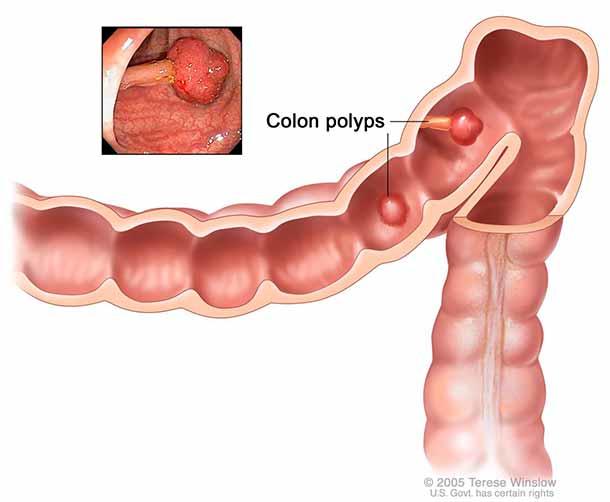
In anatomy a polyp is an abnormal growth of tissue projecting from a mucous membrane if it is attached to the surface by a narrow elongated stalk it is said to be pedunculated. The average polyp may be 1 4 inch in diameter and 1 2 inch in length. A polyp is a projection growth of tissue from the inner lining of the colon into the lumen hollow center of the colon.
A colon polyp is a small clump of cells that forms on the lining of the colon. Of course it depends on how often the person has a colonoscopy. Different types of polyps look different under the microscope.
Polyps lumps on the smooth lining of the colon or rectum are increasingly common after. Virtually all colon cancer develops from polyps in the colon. While the majority of colon cancers start as polyps only 5 10 of all polyps will become cancerous.
The level of risk depends on the size number and characteristics of the adenomatous polyps that were removed.



















/polyps-in-colon--artwork-488635669-594887b83df78c537b1a2b07.jpg)